Wi-Fi technology has come a long way since its inception, with each new generation promising faster speeds and improved performance. The two most common Wi-Fi frequencies in use today are 2.4GHz and 5GHz, with the latter often referred to as “Wi-Fi 5G.” But is Wi-Fi 5G really faster than its 2.4GHz counterpart? Let’s dive into the details to understand the speed differences between these two frequencies.
 Understanding Wi-Fi Frequencies
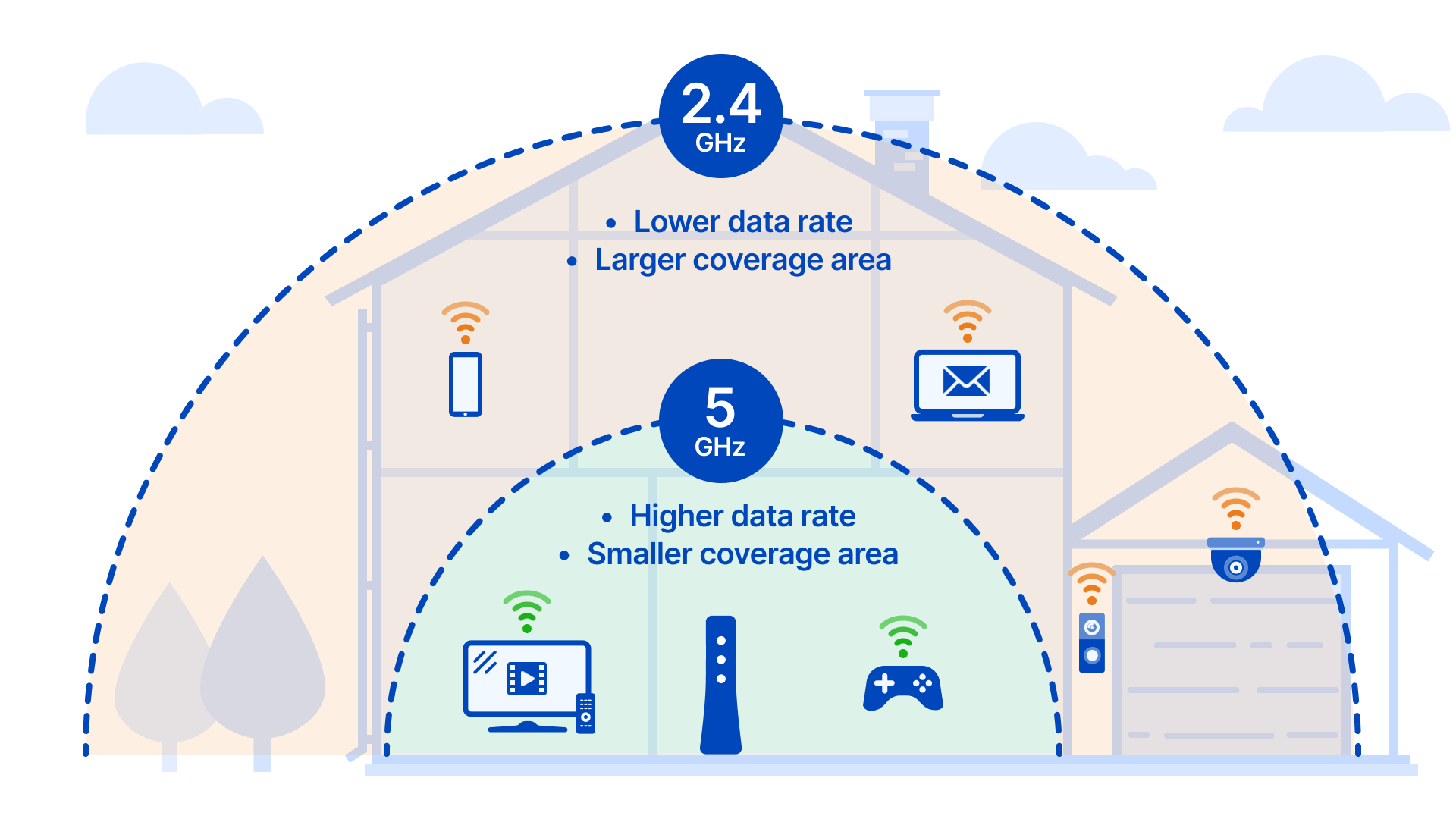
Understanding Wi-Fi Frequencies
Before we compare the speeds, it’s essential to understand the fundamental differences between the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies.
2.4GHz Frequency:
- Older technology, introduced with the 802.11b standard in 1999
- Longer range but more susceptible to interference from other devices (e.g., microwaves, cordless phones)
- Supports fewer channels (up to 14, depending on the region)
- Maximum theoretical speed of 600 Mbps (with 802.11n)
5GHz Frequency:
- Newer technology, introduced with the 802.11a standard in 1999
- Shorter range but less susceptible to interference
- Supports more non-overlapping channels (up to 25)
- Maximum theoretical speed of 6.9 Gbps (with 802.11ax or Wi-Fi 6)
Real-World Speed Differences
While the theoretical maximum speeds provide a good reference point, real-world performance can vary significantly based on various factors, such as distance from the router, obstacles, and the number of connected devices.
In general, Wi-Fi 5G (5GHz) offers faster real-world speeds than 2.4GHz networks, especially in environments with minimal interference and when devices are located closer to the router. However, the 5GHz frequency has a shorter range, which means the signal may not reach as far as the 2.4GHz frequency.
Here’s a table comparing the typical real-world speeds you can expect from each frequency:
| Frequency | Close Range (< 15 ft) | Medium Range (15-50 ft) | Long Range (> 50 ft) |
| 2.4GHz | 50-100 Mbps | 20-50 Mbps | 5-20 Mbps |
| 5GHz | 300-600 Mbps | 100-300 Mbps | 20-100 Mbps |
As you can see, the 5GHz frequency outperforms the 2.4GHz frequency at all ranges, but the performance gap widens significantly at closer distances.
Factors Affecting Wi-Fi Speed
While the frequency plays a crucial role in determining Wi-Fi speed, several other factors can also impact your network’s performance:
- Router Capabilities: The maximum speed you can achieve is limited by the capabilities of your router and its supported Wi-Fi standards (e.g., 802.11n, 802.11ac, 802.11ax).
- Device Compatibility: Your connected devices must also support the same Wi-Fi standard as your router to take advantage of the higher speeds.
- Interference: Both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies can experience interference from other wireless devices, cordless phones, microwaves, and even neighboring Wi-Fi networks.
- Network Congestion: The more devices connected to your Wi-Fi network, the more bandwidth is shared among them, potentially slowing down the overall speed.
- Physical Obstructions: Walls, floors, and other physical barriers can weaken the Wi-Fi signal, reducing the effective range and speed.
- Distance from the Router: The further you are from the router, the weaker the signal becomes, resulting in slower speeds.
To optimize your Wi-Fi speed, it’s essential to consider these factors and take appropriate measures, such as upgrading to a newer router, minimizing interference, and properly positioning your router for optimal coverage.
When to Use 2.4GHz or 5GHz
Choosing between the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies largely depends on your specific needs and environment.
Use 2.4GHz When:
- You need better range and coverage
- You have older devices that don’t support 5GHz
- You experience minimal interference in the 2.4GHz band
Use 5GHz When:
- You prioritize speed over range
- You have newer devices that support 5GHz
- You experience significant interference in the 2.4GHz band
Many modern routers support both frequencies simultaneously, allowing you to connect different devices to the most suitable band based on their capabilities and your needs.
Key Takeaways
- Wi-Fi 5G (5GHz) offers faster theoretical and real-world speeds compared to the 2.4GHz frequency, especially at closer ranges.
- However, the 5GHz frequency has a shorter range and is more susceptible to physical obstructions.
- Factors like router capabilities, device compatibility, interference, network congestion, and distance from the router can significantly impact Wi-Fi speed.
- Choosing between 2.4GHz and 5GHz depends on your specific needs, environment, and device compatibility.
- Optimizing your Wi-Fi network by upgrading hardware, minimizing interference, and proper router placement can help achieve the best possible speeds.
Conclusion
While Wi-Fi 5G (5GHz) is generally faster than the 2.4GHz frequency, the real-world performance can vary greatly depending on various factors. The choice between the two frequencies ultimately depends on your specific needs, environment, and device compatibility. By understanding the differences and optimizing your Wi-Fi network, you can ensure a faster and more reliable wireless internet experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the maximum theoretical speed of Wi-Fi 5G (5GHz)?
The maximum theoretical speed of Wi-Fi 5G (5GHz) with the latest 802.11ax standard (also known as Wi-Fi 6) is 6.9 Gbps.
- Can I use both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies simultaneously?
Yes, many modern routers support dual-band operation, allowing you to connect different devices to the most suitable frequency based on their capabilities and your needs.
- Why does the 5GHz frequency have a shorter range than 2.4GHz?
The 5GHz frequency has a shorter wavelength, which makes it more susceptible to physical obstructions and signal attenuation over longer distances.
- Do I need to upgrade my devices to take advantage of Wi-Fi 5G speeds?
Yes, both your router and connected devices must support the latest Wi-Fi standards (e.g., 802.11ac or 802.11ax) to benefit from the higher speeds offered by Wi-Fi 5G.
- Can interference affect Wi-Fi 5G speeds?
Yes, interference from other wireless devices, microwaves, and neighboring Wi-Fi networks can impact the speed and performance of both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies.
- How can I minimize interference on my Wi-Fi network?
You can minimize interference by changing the Wi-Fi channel, positioning your router away from potential sources of interference, and using a less congested frequency band (e.g., 5GHz in areas with many 2.4GHz networks).
- Is Wi-Fi 5G more secure than 2.4GHz?
No, the security of your Wi-Fi network depends on the encryption protocols and authentication methods used, not the frequency band.
- Can the distance from the router affect Wi-Fi 5G speeds?
Yes, the further you are from the router, the weaker the signal becomes, resulting in slower speeds for both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies.
- How can I improve the range of my Wi-Fi 5G network?
You can improve the range of your Wi-Fi 5G network by using a router with higher transmit power, adding range extenders or access points, and minimizing physical obstructions between the router and connected devices.
- Is Wi-Fi 5G better for streaming or gaming?
Wi-Fi 5G is generally better for streaming and gaming due to its higher speeds and lower latency, especially when devices are in close proximity to the router.
- Can I use Wi-Fi 5G for outdoor applications?
While Wi-Fi 5G has a shorter range than 2.4GHz, it can still be used for outdoor applications, but you may need additional access points or range extenders to ensure adequate coverage.
- Are there any health concerns associated with Wi-Fi 5G?
Both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies are non-ionizing radiation and are considered safe for human exposure within the recommended limits set by regulatory bodies.
- How do I know if my devices support Wi-Fi 5G?
You can check the specifications of your devices (e.g., smartphones, laptops, tablets) to see if they support the latest Wi-Fi standards, such as 802.11ac or 802.11ax, which operate on the 5GHz frequency.
- Can I use Wi-Fi 5G for Internet of Things (IoT) devices?
Yes, many IoT devices support Wi-Fi 5G, which can provide faster and more reliable connections for smart home automation, security systems, and other IoT applications.
- Is Wi-Fi 5G compatible with older Wi-Fi standards?
Yes, Wi-Fi 5G is backward compatible with older Wi-Fi standards, allowing devices that only support 2.4GHz or older 5GHz standards to connect to the network, but at lower speeds.
- How can I optimize my Wi-Fi network for the best speeds?
To optimize your Wi-Fi network for the best speeds, consider upgrading to a newer router that supports the latest Wi-Fi standards, minimizing interference, positioning the router strategically, and connecting devices to the most suitable frequency band based on their capabilities and proximity to the router.
- Can Wi-Fi 5G be used for mesh networks?
Yes, many mesh Wi-Fi systems utilize the 5GHz frequency to provide faster and more reliable connections between the individual nodes in the mesh network.
- Is Wi-Fi 5G better for large households or small offices?
Wi-Fi 5G is generally better suited for large households or small offices due to its higher speeds and ability to support more devices simultaneously without significant performance degradation.
- How does Wi-Fi 5G compare to wired Ethernet connections?
While Wi-Fi 5G offers faster speeds than previous Wi-Fi generations, wired Ethernet connections are still generally faster and more reliable, especially for applications that require consistent high-speed data transfer.
- Will Wi-Fi 5G become obsolete with the emergence of new technologies?
While newer Wi-Fi standards and technologies will continue to emerge, Wi-Fi 5G is likely to remain relevant for several years, as it provides a significant performance improvement over previous generations and supports various use cases and applications.
