In the ever-evolving world of wireless technology, the debate between 2.4GHz and 5GHz WiFi frequencies has been ongoing. Both frequencies offer distinct advantages and limitations, making it crucial to understand their differences and choose the right one for your specific needs.
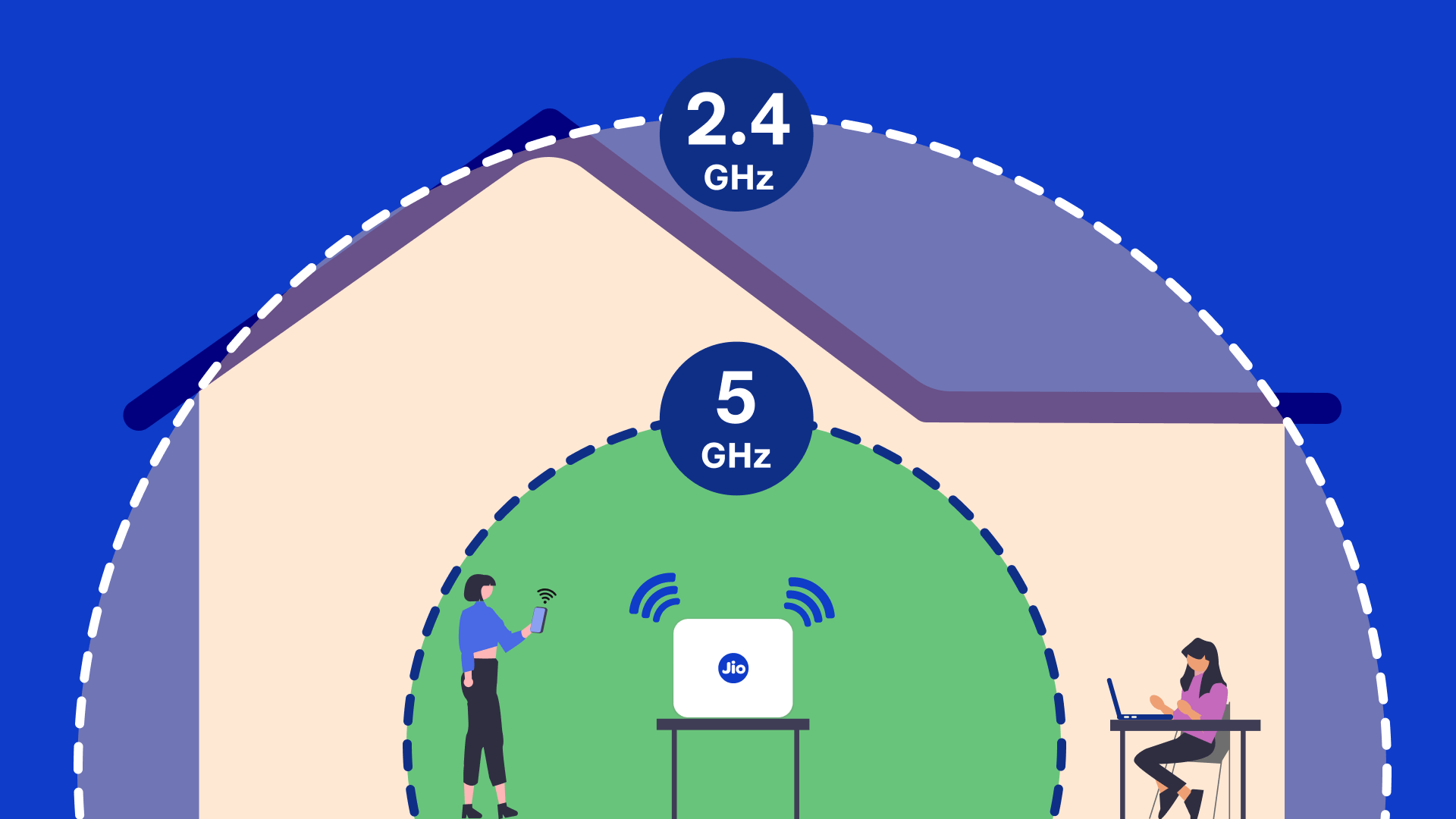
The 2.4GHz frequency band has been the traditional choice for WiFi networks, offering a longer range and better penetration through walls and obstacles. However, it is also more susceptible to interference from other devices operating on the same frequency, such as microwaves, cordless phones, and Bluetooth devices.
On the other hand, the 5GHz frequency band is newer and offers faster data transfer speeds, reduced interference, and more available channels. However, it has a shorter range and may struggle to penetrate solid obstacles like concrete walls.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each frequency is crucial for optimizing your WiFi performance and ensuring a seamless user experience.
Range and Penetration: 2.4GHz vs 5GHz
2.4GHz: The Long-Range Contender
The 2.4GHz frequency band has a longer range than its 5GHz counterpart, typically covering a larger area within a home or office. This makes it ideal for settings where devices need to be connected from various locations, including far corners or different floors.
Additionally, the 2.4GHz frequency has better penetration capabilities, allowing the signal to pass through walls, floors, and other obstacles more easily. This characteristic makes it a suitable choice for environments with multiple rooms or structural barriers.
5GHz: The Short-Range Speedster
In contrast, the 5GHz frequency band has a shorter range compared to 2.4GHz. Its signal strength diminishes more rapidly over distance, making it less effective for large areas or environments with numerous obstacles.
However, the shorter range of 5GHz can be advantageous in densely populated areas, as it reduces the likelihood of interference from neighboring WiFi networks. This characteristic makes it an attractive option for apartments, offices, or other high-density living spaces.
Speed and Bandwidth: The Need for Speed
2.4GHz: Slower but More Reliable
While the 2.4GHz frequency band offers a longer range and better penetration, it is generally slower in terms of data transfer speeds compared to the 5GHz band. This is due to the limited number of non-overlapping channels available in the 2.4GHz spectrum, leading to potential interference and reduced throughput.
However, the slower speeds of 2.4GHz can be an advantage in certain scenarios where reliability and stable connections are more important than raw speed, such as for Internet of Things (IoT) devices or applications that don’t require high bandwidth.
5GHz: Blazing-Fast Performance
The 5GHz frequency band is designed to deliver faster data transfer speeds, making it ideal for bandwidth-intensive applications like streaming high-definition video, online gaming, or transferring large files. With more available non-overlapping channels, the 5GHz band offers less interference and higher throughput, resulting in a smoother and more responsive user experience.
Additionally, the 5GHz band supports newer WiFi standards, such as 802.11ac and 802.11ax (WiFi 6), which offer even higher theoretical speeds and improved performance compared to their predecessors.
Interference and Overcrowding: The Bane of WiFi
2.4GHz: Crowded and Noisy
One of the major drawbacks of the 2.4GHz frequency band is its susceptibility to interference from various sources, including microwaves, cordless phones, Bluetooth devices, and even other WiFi networks in the vicinity. This interference can lead to reduced performance, dropped connections, and overall degradation of the user experience.
Furthermore, the limited number of non-overlapping channels in the 2.4GHz band exacerbates the issue of overcrowding, especially in densely populated areas where multiple WiFi networks compete for the same channels.
5GHz: Less Congestion, More Harmony
In contrast, the 5GHz frequency band is less crowded and has more available non-overlapping channels, making it less prone to interference from other devices or neighboring WiFi networks. This characteristic makes it a more suitable choice for environments with multiple WiFi access points or high network traffic.
However, it’s important to note that while the 5GHz band is less susceptible to interference from common household devices, it can still experience performance degradation due to obstacles or interference from other 5GHz sources, such as neighboring WiFi networks or wireless cameras.
Compatibility and Device Support
2.4GHz: Universal Compatibility
One of the major advantages of the 2.4GHz frequency band is its universal compatibility with a wide range of devices, including older hardware and legacy systems. Most WiFi-enabled devices, from smartphones and laptops to IoT devices and smart home gadgets, support the 2.4GHz band, ensuring seamless connectivity and interoperability.
5GHz: Varying Device Support
While the 5GHz frequency band offers superior performance and reduced interference, not all devices are capable of operating on this band. Older devices or those with limited hardware capabilities may only support the 2.4GHz band, potentially limiting their ability to take advantage of the faster speeds and improved performance offered by the 5GHz band.
It’s crucial to ensure that all devices in your network are compatible with the 5GHz band before transitioning to this frequency, as mixing devices with different band support can lead to connectivity issues and suboptimal performance.
Optimal Use Cases: Finding the Right Fit
2.4GHz: Ideal for General Use and IoT Devices
The 2.4GHz frequency band is often the preferred choice for general WiFi usage, such as browsing the internet, checking emails, or streaming standard-definition content. Its longer range and better penetration make it suitable for larger homes or offices, where devices need to be connected from various locations.
Additionally, the 2.4GHz band is well-suited for Internet of Things (IoT) devices and smart home gadgets that prioritize reliable connectivity over high-speed data transfer. These devices typically have lower bandwidth requirements and benefit from the extended range and obstacle penetration capabilities of the 2.4GHz band.
5GHz: Best for High-Bandwidth Applications and Dense Environments
The 5GHz frequency band shines when it comes to high-bandwidth applications, such as streaming high-definition video, online gaming, or transferring large files. Its faster data transfer speeds and reduced interference make it the ideal choice for these demanding tasks, ensuring a smooth and responsive user experience.
Moreover, the 5GHz band is particularly well-suited for densely populated areas, such as apartments, offices, or public spaces, where multiple WiFi networks operate in close proximity. Its shorter range and increased number of non-overlapping channels help mitigate interference and overcrowding, resulting in better overall performance.
Key Takeaways
- The 2.4GHz frequency band offers a longer range, better penetration through obstacles, and universal compatibility with most devices, making it suitable for general WiFi usage and IoT devices.
- The 5GHz frequency band provides faster data transfer speeds, reduced interference, and more available non-overlapping channels, making it ideal for high-bandwidth applications and dense environments.
- Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each frequency band is crucial for optimizing WiFi performance and ensuring a seamless user experience based on your specific needs.
- Compatibility with devices is an important consideration when choosing between 2.4GHz and 5GHz, as not all devices support the 5GHz band.
- The choice between 2.4GHz and 5GHz ultimately depends on factors such as range requirements, bandwidth demands, interference levels, and the types of devices in your network.
Conclusion
In the battle between 2.4GHz and 5GHz WiFi frequencies, there is no clear-cut winner. Both frequencies have their unique strengths and weaknesses, catering to different use cases and environments.
The 2.4GHz band excels in providing a longer range, better penetration through obstacles, and universal compatibility with most devices, making it a reliable choice for general WiFi usage and IoT devices. However, it is more susceptible to interference and overcrowding, which can impact performance.
On the other hand, the 5GHz band offers faster data transfer speeds, reduced interference, and more available non-overlapping channels, making it the ideal choice for high-bandwidth applications and densely populated areas. However, its shorter range and potential compatibility issues with older devices should be considered.
Ultimately, the decision between 2.4GHz and 5GHz should be based on a careful assessment of your specific needs, including range requirements, bandwidth demands, interference levels, and the types of devices in your network. In many cases, a dual-band router or access point that supports both frequencies can provide the best of both worlds, allowing you to leverage the strengths of each band as needed.
By understanding the differences between 2.4GHz and 5GHz WiFi frequencies, you can make an informed decision and optimize your wireless network for peak performance, ensuring a seamless and enjoyable user experience.
Frequently Asked Questions
- Can I use both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies simultaneously?
Yes, modern routers and access points often support dual-band operation, allowing you to connect devices to both the 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies simultaneously. This can provide the best of both worlds, with faster 5GHz speeds for high-bandwidth devices and longer 2.4GHz range for extended coverage.
- Will my older devices work on the 5GHz band?
Not all older devices are compatible with the 5GHz frequency band. Devices that were manufactured before the widespread adoption of 5GHz WiFi may only support the 2.4GHz band. It’s important to check the specifications of your devices to ensure compatibility before attempting to connect them to a 5GHz network.
- Is the 5GHz band more secure than 2.4GHz?
While the 5GHz band is not inherently more secure than the 2.4GHz band, it does offer some potential security advantages. The shorter range of the 5GHz signal makes it less likely to be intercepted by neighboring networks or unauthorized users. Additionally, the higher number of available channels reduces the likelihood of interference and potential eavesdropping.
- Can I use the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands simultaneously on the same device?
Yes, many modern devices are capable of connecting to both the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands simultaneously, a feature known as “band steering” or “band switching.” This allows the device to intelligently switch between the two bands based on factors such as signal strength, interference, and bandwidth requirements, providing a seamless user experience.
- Does the 5GHz band have better range outdoors?
No, the 5GHz band generally has a shorter range compared to the 2.4GHz band, especially in outdoor environments. The higher frequency of the 5GHz signal makes it more susceptible to attenuation by obstacles and atmospheric conditions, resulting in a reduced effective range outdoors.
- Can I extend the range of my 5GHz network?
Yes, there are several ways to extend the range of a 5GHz network, including using high-gain antennas, strategically placing additional access points or wireless repeaters, and reducing obstacles or interference sources in the signal path.
- Is the 2.4GHz band more affected by interference from neighboring networks?
Yes, the 2.4GHz band is more prone to interference from neighboring WiFi networks due to the limited number of non-overlapping channels available. In densely populated areas, multiple networks may compete for the same channels, leading to interference and performance degradation.
- Can I use the 5GHz band for Internet of Things (IoT) devices?
While the 5GHz band is generally better suited for high-bandwidth applications, some IoT devices may support it. However, many IoT devices prioritize range and reliable connectivity over speed, making the 2.4GHz band a more common choice for these types of devices.
- Does the 5GHz band consume more power than 2.4GHz?
In general, the 5GHz band does consume slightly more power than the 2.4GHz band due to the higher frequency and shorter wavelength. This can result in slightly reduced battery life for mobile devices connected to a 5GHz network. However, the power consumption difference is typically negligible for most devices.
- Can I switch between 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequencies on my router?
Most modern routers and access points allow you to enable or disable the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands individually, giving you the flexibility to choose which frequencies to broadcast based on your needs. However, it’s generally recommended to keep both bands enabled to support a wider range of devices and use cases.
- Is the 5GHz band more susceptible to interference from weather conditions?
Yes, the higher frequency of the 5GHz band makes it more susceptible to interference from atmospheric conditions, such as rain or humidity, compared to the 2.4GHz band. This can result in reduced range and potential performance degradation during adverse weather conditions.
- Can I use the 5GHz band for long-distance WiFi links?
While the 5GHz band can be used for long-distance WiFi links, it may not be the optimal choice due to its shorter range and higher susceptibility to obstacles and atmospheric conditions. The 2.4GHz band is generally preferred for long-distance wireless links due to its better propagation characteristics.
- Will my WiFi performance improve if I switch to the 5GHz band?
Switching to the 5GHz band can potentially improve your WiFi performance, especially for high-bandwidth applications or in areas with significant interference on the 2.4GHz band. However, the actual performance improvement will depend on factors such as device compatibility, distance from the access point, and the presence of obstacles or interference sources.
- Can I use the 5GHz band for wireless video streaming?
Yes, the 5GHz band is well-suited for wireless video streaming, particularly for high-definition or 4K content. The higher data transfer speeds and reduced interference of the 5GHz band can provide a smoother and more reliable streaming experience compared to the 2.4GHz band.
- Is the 2.4GHz band better for smart home devices?
In many cases, the 2.4GHz band is preferred for smart home devices and IoT gadgets due to its longer range and better penetration through walls and obstacles. These devices often prioritize reliable connectivity over high-speed data transfer, making the 2.4GHz band a more suitable choice.
- Can I use the 5GHz band for wireless gaming?
Yes, the 5GHz band is an excellent choice for wireless gaming, as it offers lower latency and faster data transfer speeds compared to the 2.4GHz band. This can result in a more responsive and smoother gaming experience, especially for online multiplayer games or those with high-bandwidth requirements.
- Does the 5GHz band have better throughput than 2.4GHz?
Yes, the 5GHz band generally offers higher theoretical throughput and data transfer speeds compared to the 2.4GHz band. This is due to the higher number of available non-overlapping channels and support for newer WiFi standards like 802.11ac and 802.11ax (WiFi 6).
- Can I use the 2.4GHz band for file transfers?
While the 2.4GHz band can be used for file transfers, it may not be the optimal choice for large file transfers or high-speed data transfers. The 5GHz band, with its faster data transfer speeds and reduced interference, is generally better suited for these types of tasks.
- Is the 5GHz band more energy-efficient than 2.4GHz?
There is no significant difference in energy efficiency between the 2.4GHz and 5GHz bands. The power consumption of WiFi devices is primarily determined by factors such as hardware design, signal strength, and data transfer rates, rather than the specific frequency band being used.
- Can I use the 2.4GHz band for wireless bridge connections?
Yes, the 2.4GHz band is often used for wireless bridge connections, particularly for long-distance links or point-to-point connections. The longer range and better penetration capabilities of the 2.4GHz band make it a suitable choice for bridging networks across buildings or over large outdoor areas.
